Lenz’s Law
Lenz’s Law: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Lenz's Law & Lenz's Law and Law of Conservation of Energy etc.
Important Questions on Lenz’s Law
A magnet falling vertically under gravity, passes through a metal ring on its way. Which of the following is true about the acceleration of the magnet ? (where denotes the acceleration due to gravity)
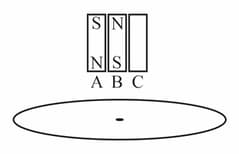
Two bar magnets A and B, and a non-magnetic bar , all of same mass and dimensions, are dropped in an identical manner one by one through the center of a copper loop held horizontally (as shown in the figure). The times taken by the bars , and to reach the ground are , and , respectively. Which of the following relations is correct?
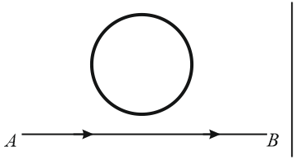
An electron moves along the line which lies in the same plane as a circular loop of conducting wires as shown in the diagram. What will be the direction of current induced if any, in the loop?
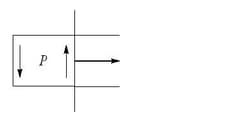
A movable wire is moved to the right, that causes an anti-clock-wise induced current as shown in the figure. The direction of magnetic induction in the region P points
Lenz 's law used to find out the direction of
Lenz's law is a consequence of the law of conservation of
A small bar magnet is falling vertically downward through a fixed horizontal conducting ring as shown. If be the acceleration due to gravity, then the acceleration of will be
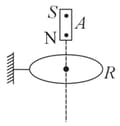
A to B are two metallic rings placed at opposite sides of an infinitely long straight conducting wire as shown. When the current in the wire is slowly decreased, what will be the direction of induced current ?

A metallic ring with a small cut is held horizontally and a magnet is then allowed to fall vertically through the ring. Then what must have been the acceleration of the magnet ?
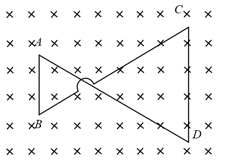
As shown in the above figure, a magnetic field is directed into the plane of the coil . If the field is increasing at a constant rate, then find the directions of induced currents in wires and , respectively:
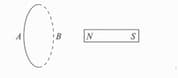
As shown in the above figure, a magnet is pushed towards a fixed ring along its axis until the magnet passes through the ring. Now, choose the correct statement from the following:
Lenz's law is based on conservation of
The Lenz law is consequence of conservation of
Two coils, carrying currents in opposite directions are placed co-axially with their centres at some finite separation. If they are brought closer to each other, then the current flowing in them should be:
In which direction will the induced current flow through the loop, at time ?
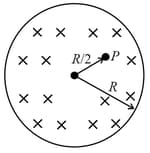
A uniform but time varying magnetic field is present in a cylindrical region of radius as shown in figure. The force on an electron at P at is
Which of the following statements is not correct?
A solenoid is connected to a battery so that a steady current flows through it. If an iron core is inserted into the solenoid, the current will
If a magnet is dropped through a vertical hollow copper tube, then
A metallic ring of radius and resistance is held fixed with its axis along a spatially uniform magnetic field whose magnitude is Neglect gravity. Then,
